Lung cancer remains one of the most serious and life-threatening diseases in the United States. According to the American Cancer Society, it is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths for both men and women, accounting for nearly one in five cancer deaths. Yet, despite its prevalence, early awareness, lifestyle changes, and timely medical screening can save lives. This article explores what lung cancer is, its causes, symptoms, risk factors, treatment options, and—most importantly—how you can take proactive steps to protect your lungs.
What Is Lung Cancer?
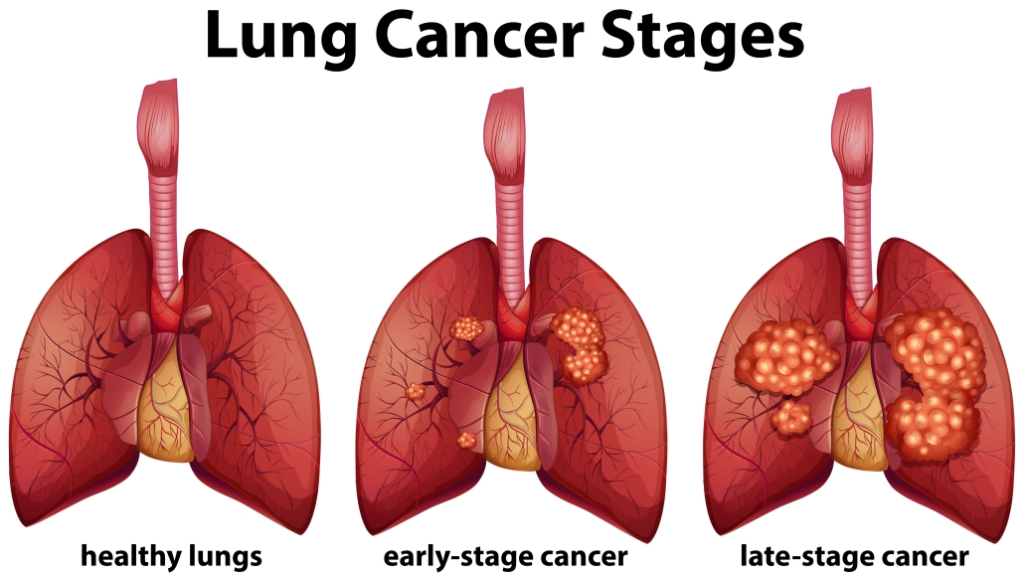
Lung cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably and form tumors that interfere with normal breathing. These cancerous cells can eventually spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body such as the brain, bones, and liver, making treatment more challenging.
There are two main types of lung cancer:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) – The most common form, accounting for about 85% of all cases. It generally grows and spreads more slowly.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) – A more aggressive type that spreads rapidly and is closely linked to smoking.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Lung cancer often develops silently in its early stages, which is why many people are diagnosed only after the disease has advanced. However, being aware of the warning signs can make a big difference.
Common symptoms include:
- A persistent cough that doesn’t go away
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored mucus
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue
If you experience any of these symptoms for more than a few weeks—especially if you smoke or have a history of exposure to harmful substances—see your doctor for an evaluation.
What Causes Lung Cancer?
While smoking remains the leading cause, it’s not the only factor. Up to 20% of people diagnosed with lung cancer have never smoked.
Major causes and risk factors include:
- Cigarette smoking: Responsible for around 80–90% of all lung cancer cases.
- Secondhand smoke exposure: Even living with a smoker increases your risk.
- Radon gas: A naturally occurring radioactive gas found in many U.S. homes.
- Air pollution: Long-term exposure to polluted air or industrial chemicals can damage lung tissue.
- Family history and genetics: Some people inherit genetic mutations that make them more susceptible.
How Is Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
Early detection saves lives. Low-dose CT (LDCT) scans are now widely recommended for people at high risk—especially those aged 50–80 with a long history of smoking.
Diagnosis usually involves:
- Imaging tests: Chest X-rays or CT scans to locate abnormal growths.
- Biopsy: A small sample of tissue is taken for examination.
- Molecular testing: Determines whether specific gene mutations are present to guide targeted therapy.
Treatment Options
Lung cancer treatment depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. The main treatment options include:
- Surgery: To remove the tumor and surrounding tissue if detected early.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that kill rapidly dividing cells, often used for advanced stages.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific genetic mutations driving the cancer’s growth.
- Immunotherapy: Helps the body’s immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
In recent years, advances in targeted therapy and immunotherapy have dramatically improved survival rates, especially for patients diagnosed early or with specific genetic markers.
Foods and Habits That Support Lung Health
While diet alone cannot prevent or cure lung cancer, healthy nutrition can support your immune system, help your body fight inflammation, and improve treatment outcomes.
Best foods for lung health:
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and broccoli are rich in antioxidants like vitamins C and E.
- Citrus fruits: Oranges, lemons, and grapefruits help protect lung tissue.
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines contain omega-3 fatty acids that reduce inflammation.
- Tomatoes: Lycopene, found in tomatoes, may help lower the risk of lung damage.
- Green tea: Contains polyphenols that can slow the growth of cancer cells.
Habits that can make a difference:
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Test your home for radon gas.
- Exercise regularly to strengthen your lungs.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Get regular screenings if you’re at high risk.
When to See a Doctor
If you have a history of smoking or long-term exposure to pollutants and experience persistent coughing, shortness of breath, or chest discomfort, don’t wait. Early detection through screening can catch lung cancer when it’s still treatable.
Conclusion: Awareness Is the First Line of Defense
Lung cancer doesn’t always show symptoms until it’s advanced—but that doesn’t mean it’s unstoppable. By understanding the risks, taking preventive steps, and making smart lifestyle choices, you can protect your lungs and your life.
Whether it’s quitting smoking, improving air quality at home, or getting screened early, every action counts. Remember, your lungs are your body’s lifeline—treat them with the care they deserve.